1. Fenchone
Biological Sources:
Fenchone is a monoterpenoid found in several essential oils. It is most commonly derived from Foeniculum vulgare (fennel) and Lavandula angustifolia (lavender). It is also present in the oils of Thuja plicata (Western red cedar) and Piper angustifolium.
Chemical Structure:
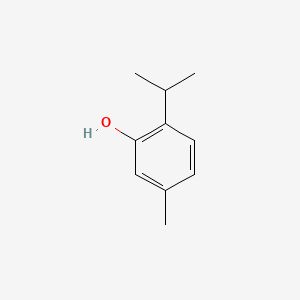
Fenchone has a bicyclic structure with a ketone group. It is a monoterpene ketone, with the molecular formula C₁₀H₁₆O. Its structure includes two fused cyclohexane rings, and the ketone functional group is located on one of these rings.- IUPAC Name: 1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-norbornanone
- Structure:
2. Geraniol
Biological Sources:
Geraniol is a monoterpenoid and alcohol found in the essential oils of several aromatic plants. Common sources include Cymbopogon species (lemongrass), Pelargonium graveolens (geranium), Rosa species (rose), and Monarda didyma (bee balm).Chemical Structure:
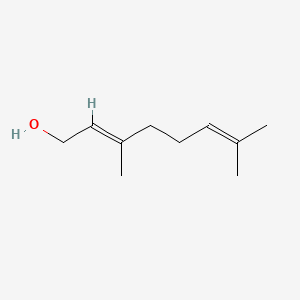
Geraniol is an acyclic monoterpene alcohol with the molecular formula C₁₀H₁₈O. It has a long chain with a hydroxyl group (-OH) at one end.- IUPAC Name: 3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-ol
- Structure:
3. Eugenol
Biological Sources:
Eugenol is a phenylpropene, a type of phenolic compound, found predominantly in Syzygium aromaticum (clove), Ocimum basilicum (basil), Cinnamomum verum (cinnamon), and Pimenta dioica (allspice). It is the main active ingredient in clove oil.Chemical Structure:
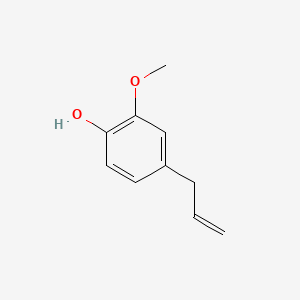
Eugenol is an allyl chain-substituted guaiacol (a phenolic compound) with the molecular formula C₁₀H₁₂O₂. It has a hydroxyl group (-OH) and a methoxy group (-OCH₃) attached to a benzene ring.- IUPAC Name: 2-Methoxy-4-(prop-2-en-1-yl)phenol
- Structure:
These compounds are widely studied for their aromatic properties and use in perfumes, food flavoring, and medicine.








0 Comments
Thanks for your feedback, i'll get back to you soon.