Artemisinin and Taxol are two of the most significant natural compounds in modern medicine, each derived from plants and utilized extensively in treating life-threatening diseases. Both compounds highlight the importance of plant-based pharmacology and have led to advancements in the treatment of malaria and cancer.
Biological Source:
Chemical Nature:
- Class: Sesquiterpene lactone.
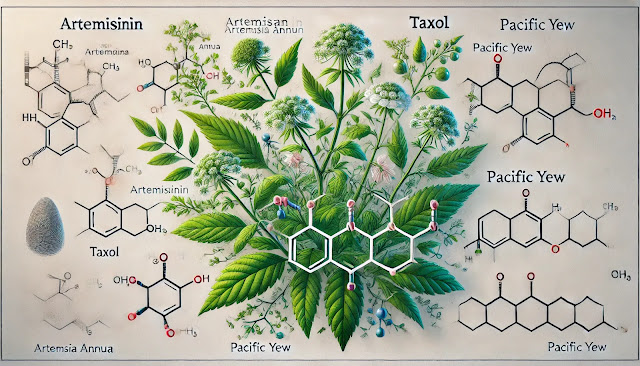
- Structure: Artemisinin contains an unusual peroxide bridge, which is crucial for its biological activity. Its chemical formula is C₁₅H₂₂O₅.
- Structure Features:
- It has a trioxane ring structure, which is rare among natural compounds.
- The endoperoxide linkage (–O–O–) is responsible for its antimalarial properties.
Uses:
- Antimalarial Drug: Artemisinin and its derivatives (e.g., artesunate, artemether) are the basis of artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) for the treatment of malaria, especially caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
- Antiparasitic Activity: Artemisinin also has potential activity against other parasites and some viruses, although its primary use remains in malaria treatment.
Taxol (Paclitaxel)
Biological Source:
Taxol is a diterpenoid compound isolated from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, Taxus brevifolia. It can also be found in other species of Taxus, and now is primarily produced through semi-synthesis from 10-deacetylbaccatin III, which is obtained from the needles of the European yew (Taxus baccata).
Chemical Nature:
- Class: Diterpene alkaloid.
- Structure: The chemical formula of taxol is C₄₇H₅₁NO₁₄.
- Structure Features:
- It has a complex polycyclic structure, consisting of a taxane ring system.
- It contains an ester side chain at C-13 that is crucial for its bioactivity.
Uses:
- Anticancer Drug: Paclitaxel is widely used in chemotherapy for various cancers, including ovarian, breast, and non-small cell lung cancer. It works by stabilizing microtubules, which inhibits their disassembly and effectively blocks cell division.
- Cell Cycle Arrest: It induces apoptosis (programmed cell death) by preventing the normal breakdown of microtubules during cell division.
Both artemisinin and taxol are important natural products that have had a profound impact on modern medicine, especially in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology.







0 Comments
Thanks for your feedback, i'll get back to you soon.